- 選択してください
超高密度磁気記録技術の開発
マイクロ波アシスト磁化反転(MAS)
ハードディスクドライブ(HDD) では、情報が小さな磁石の向きとして記録されます.社会の情報量は爆発的に増加しており、さらなる大容量化が求められています。マイクロ波アシスト磁化反転は、GHz帯の高周波磁場を印加により磁化の反転を容易にでき、記録の安定性と大容量化を両立できる技術として注目されています。本グループでは、高周波磁場の振幅や周波数、印加時間と磁化反転挙動の関係を研究し、情報インフラを支える技術開発に取り組んでいます。
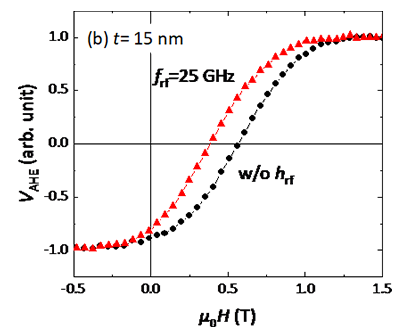
周波数25GHzの高周波磁場印加によるCoCrPt-SiO2グラニュラー薄膜の反転磁場の減少
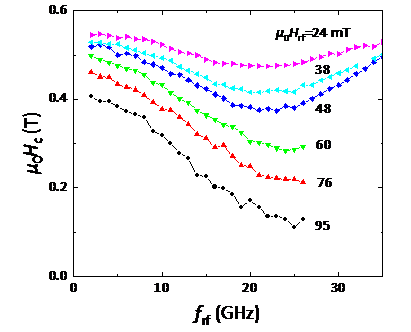
CoCrPt-SiO2グラニュラー薄膜の反転磁場の高周波磁場周波数依存性
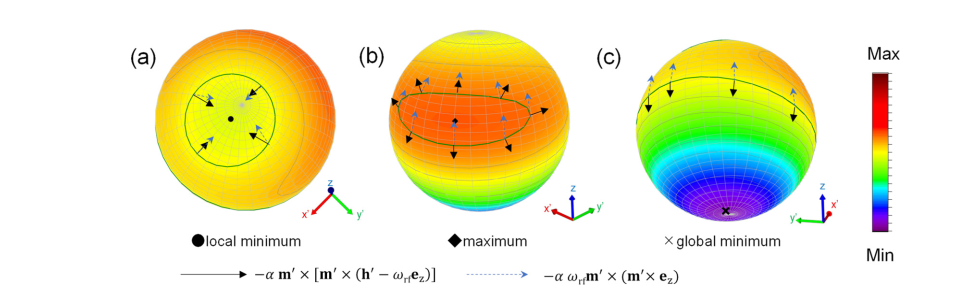
高周波磁場の周波数によって変化する実効ポテンシャルの様子
Microwave assisted switching (MAS)
Digital information is recorded as the magnetization direction of nanoparticle in Hard disk drives (HDD). In order to manage explosive increase in the amount of information, there is an urgent demand for increasing its capacity. Microwave-assisted magnetization switching is a candidate technology to realize both large capacity and stability, in
which magnetization switching field for recording is reduced by applying a high-frequency magnetic field in the GHz range. Our group is investigating magnetization reversal behavior under various microwave field conditions to develop to support information infrastructure.
[1] S. Okamoto, N. Kikuchi, M. Furuta, O Kitakami and T. Shimatsu, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 48, 353001 (2015).
[2] N. Kikuchi, K. Sato, S. Okamoto, T. Shimatsu, H. Suto, Phys. Rev. B, 105, 054430 (2022).
- 選択してください
